1-6 Protocols and Layers
Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All Rights Reserved.
mediaplayer.pearsoncmg.com
Networks Need Modularity

- We need a form of modularity, to help manage complexity and support reuse
Protocols and Layers
- Protocols and layering is the main structuring method used to divide up network functionality
- Each instance of a protocol talks virtually to its peer using the protocol
- Each instance of a protocol uses only the services of the lower layer

- Protocols are horizontal, layers are vertical
- Instance of protocol X 간에는 직접적으로 통신을 할 수 없기 때문에 더 낮은 layer인 Protocol Y의 서비스를 통해 간접적으로 통신한다
- 그렇다면 Instance of protocol Y 간에는 어떻게 직접적으로 통신을 하는 것인가?

- Set of protocols in use is called a protocol stack
- 계속 하단의 protocol이 제공하는 서비스를 사용하다보면 결국 wire로 연결된 Physical medium을 통해 메세지를 전송받을 수 있다

- 802.11 : Wi-Fi 규격
Encapsulation
- Encapsulation is the mechanism used to effect protocol layering
- Lower layer wraps higher layer content, adding its own information to make a new message for delivery
- Like sending a letter in an envelope; postal service doesn't look inside
- Message "on the wire" begins to look like an onion
- Lower layers are outermost (가장 바깥쪽)


- Normally draw messages like this
- Each layer adds its own header

- More involved in practice
- Trailers as well as headers, encrypt/compress contents
- Segmentation (divide long message) and reassembly
Demultiplexing
- Incoming message must be passed to the protocols that it uses

- Done with demultiplexing keys in the headers
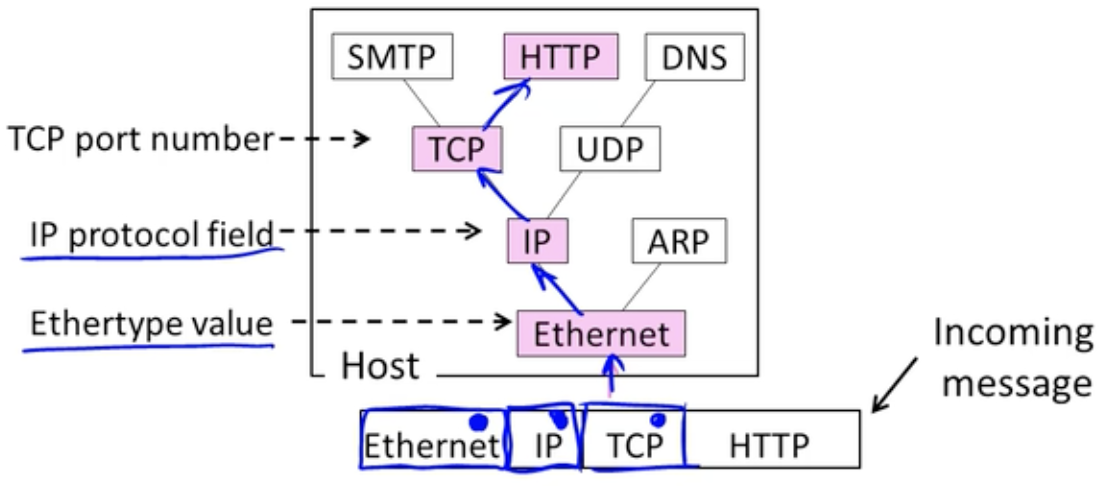
- Ethernet header에 IP protocol로 향하라는 키가 존재한다
- 마찬가지로 IP header에 TCP protocol로 향하라는 키가 존재한다
- 마찬가지로 TCP header에 HTTP의 port 번호가 존재한다
- 위의 키를 demultiplexing key라고 부른다
Advantage of Layering
- Information hiding and reuse

- Using information hiding to connect different systems

- 중계기가 존재하면 다른 프로토콜 시스템간에도 통신이 가능하다
- 바로 윗 계층까지는 변경되지만 그 상단의 데이터는 전혀 변경되지 않는다 (핑크색 영역)
Disadvantage of Layering
- Adds overhead
- But minor for long messages
- Hides information
- App might care whether it is running over wired or wireless!
1-7 Reference Models
Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All Rights Reserved.
mediaplayer.pearsoncmg.com
What functionality should we implement at which layer?
- This is a key design question
- Reference models provide frameworks that guide us
OSI "7 layer" Reference Model
- A principled, international standard, to connect systems
- Influential, but not used in practice (Woops)

- Session 역할 : 여러 컴포넌트를 종합하여 하나로 합치는
Internet Reference Model
- A four layer model based on experience; omits some OSI layers and uses IP as the network layer

- Presentation, Session 계층의 역할은 중요하지만 layer model에서는 큰 의미가 없으므로 없다

- IP is the "narrow waist" of the internet
- Supports many different links below and apps above
- 즉, 다시 말해서 IP 프로토콜은 유일하므로 다른 어떤 시스템 구성이어도 Internet layer를 통해 통신이 가능하다
Standards Bodies
- Where all the protocols come from!
- Focus in on iteroperability (상호 운용성)

Layer-based Names

- Packet은 Network 계층에서의 데이터 단위로서의 의미 뿐만 아니라 Segment, Frame을 포괄하는 데이터 단위로서도 사용되므로 주의하자


A Note About Layers
- They are guidelines, not strict
- May have multiple protocols working together in one layer
- May be difficult to assign a specific protocol to a layer
1-8 History of the Internet
Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All Rights Reserved.
mediaplayer.pearsoncmg.com
Rough Internet Timeline

The Beginning - ARPANET

- ARPANET의 목적은 리소스 공유였으나 email이 주된 사용 목적이 되었다
ARPANET - Influences


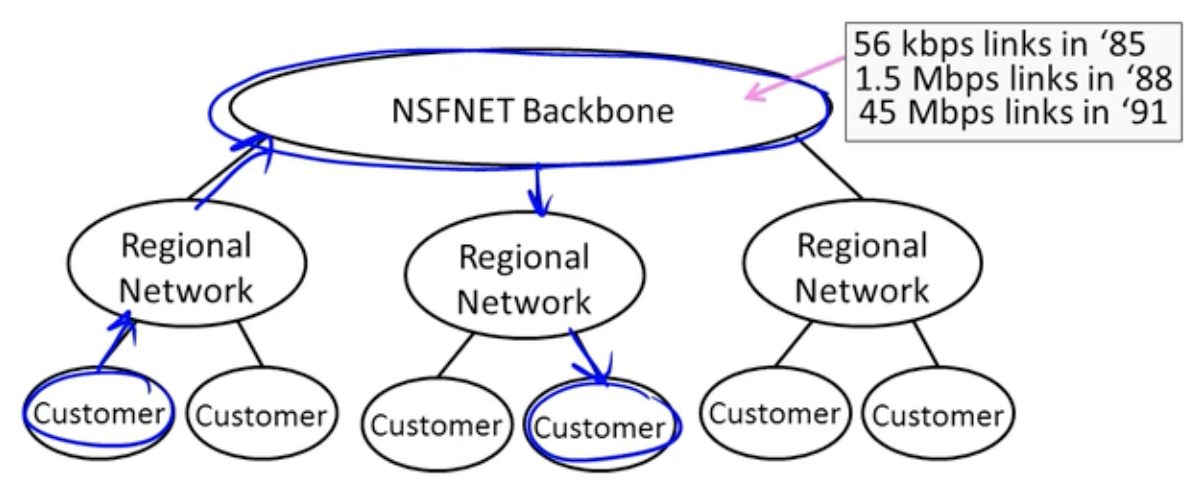
Growing Up - NSFNET

Early Internet Architecture
- Hierarchical, with NSFNET as the backbone
Modern Internet - Birth of the Web

Modern Internet Architecture
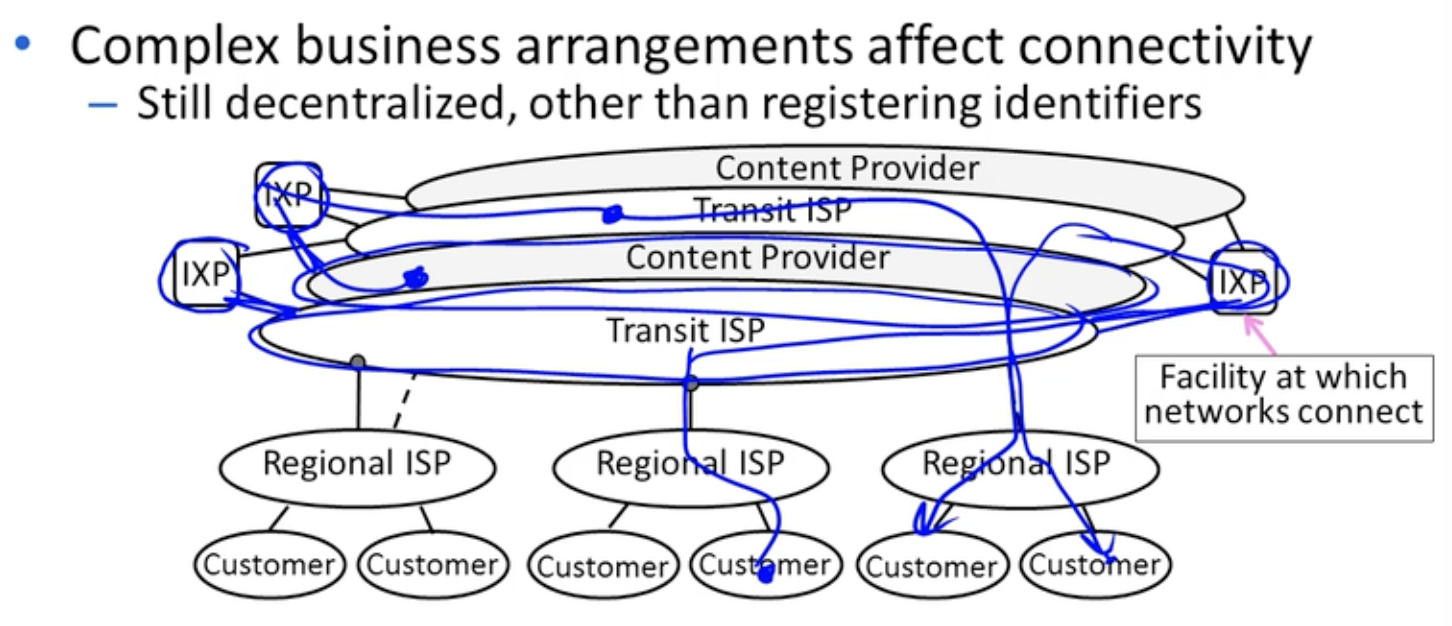
- IXP 연결을 통해 Transit ISP와 Content Provider간의 데이터 통신이 가능해졌고, Backbone 없이 Content Provider가 제공하는 컨텐츠를 Customer가 제공받거나 Customer 상호간에 데이터를 주고 받는 것이 가능해졌다
1-9 Lecture Outline
Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All Rights Reserved.
mediaplayer.pearsoncmg.com
Done - Protocols and Layering
앞으로 내우게 될 내용들
1. Course Reference Model

2. Lecture Progression (진행)

'Computer Science Lectures > Computer Networks - UW' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lecture 3b-1 ~ 3b-8: Link Layer, Part B (0) | 2022.12.04 |
|---|---|
| Lecture 3a.1 ~ 3a.5: Link Layer, Part A (0) | 2022.11.27 |
| Lecture 2.1 ~ 2.5: Physical Layer (0) | 2022.11.23 |
| Lecture 1.3 ~ 1.5: Introduction, Protocols and Layering (0) | 2022.11.13 |
| Lecture 1.1 ~ 1.2: Introduction, Protocols and Layering (1) | 2022.11.13 |